Edit a Rubric
What is a Rubric?
When importing a rubric into a course in Brightspace, you can add a pre-made assessment matrix that you can then link to assignments, discussions, or quizzes. This way, both you and your students can clearly see what is being assessed.
Navigate to Rubrics
- Click on ‘Course Admin’ in the navigation bar of the course you want to edit.
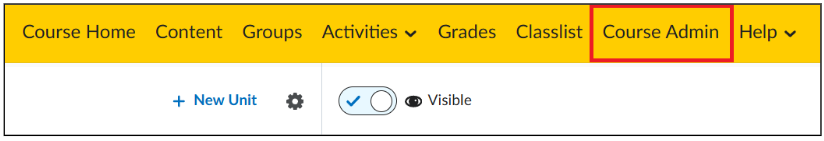
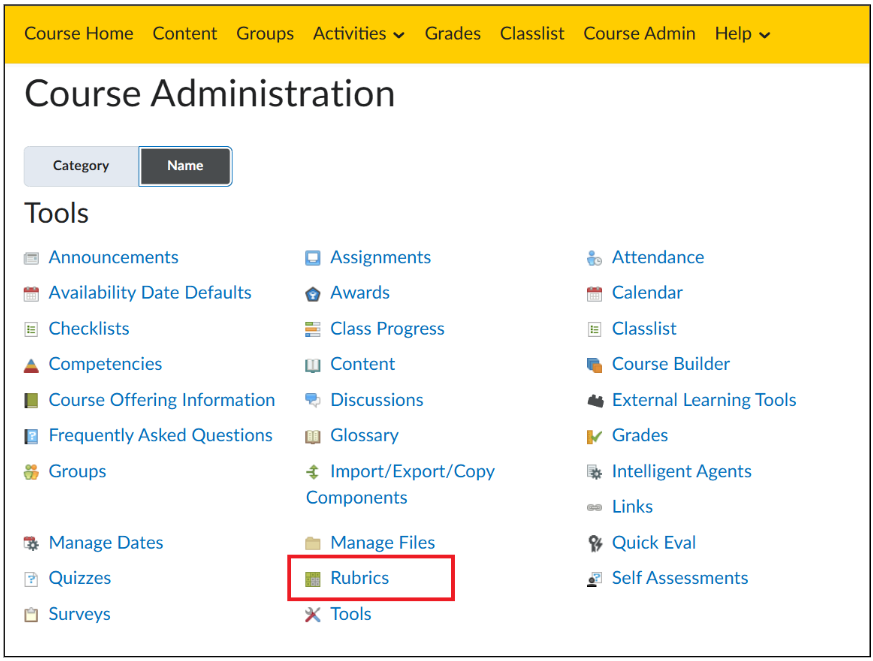
- Click on ‘Name’ on the top left and navigate to ‘Rubrics’.
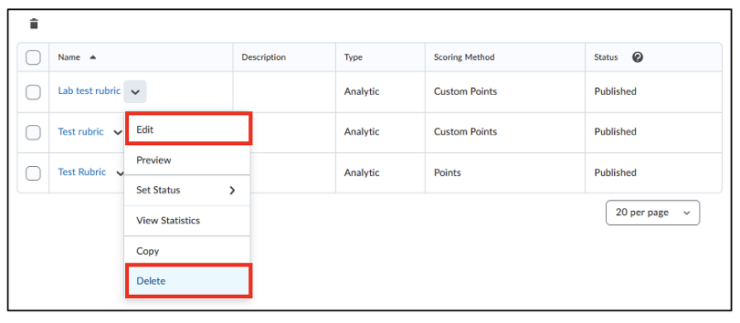
- Click on the arrow next to rubric you want to change.
- If you want to delete a rubric, click on the arrow next to the rubric in the Rubrics menu and click on ‘Delete’.
- If you want to edit a rubric, click on the arrow next to the rubric in the Rubrics menu and click on ‘Edit’.
On the Edit page of the rubric there are several options:
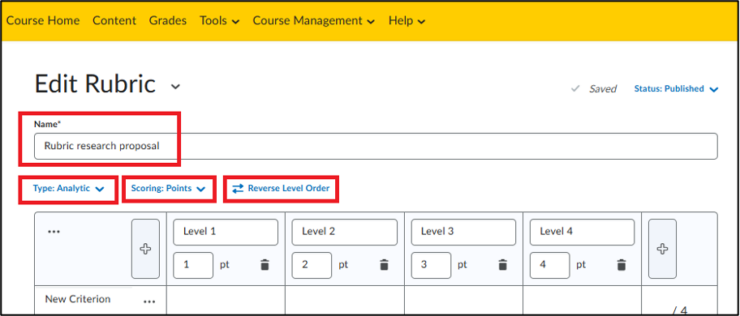
- Under ‘Name’ , you can change the name of your assessment rubric. This is useful to keep an overview and to easily find rubrics.
- Under ‘Type’, there is a choice between ‘Analytic’ and ‘Holistic’.
- Analytic is a rubric type in which you assess each criterion separately. This is more useful if you want to provide detailed feedback on multiple aspects of an assignment (e.g., grade content, structure, language separately).
- Holistic is a rubric type in which you give one general assessment based on an overall impression, without a breakdown per criterion. This is useful for quick assessments, for example with a short assignment that only scores sufficient or insufficient without much further depth.
- Under ‘Scoring’ there is a choice between ‘Points’, ‘No points’ and ‘Custom Points’.
- Points means that each achievement level has a fixed point value, for example 1, 2, 3 and 4. If something is ‘bad’, it scores 1 point. Is something ‘mediocre’, it scores 2 points. ‘Sufficient’ would then be 3 points and ‘Good’ 4 points.
- No Score means that only labels or descriptions are attached to the achievement levels, so no points are awarded. This is useful for when you give a qualitative assessment without grades.
- Custom Points means that you can set a different number of points for each assessment criterion. This is useful if you want to check a certain part of the submitted work as more important. For example, the ‘theoretical framework’ component can be weighted with 2, 4, 6, or 8 points for ‘poor’, ‘moderate’, ‘sufficient’ or ‘good’, so that it weighs twice as much as, for example, the ‘introduction’ component.
- With ‘Reverse Level Order’, you can reverse the order of the achievement levels. This is useful for assessors who prefer to work from low to high, or if this is better suited to your program’s assessment method.
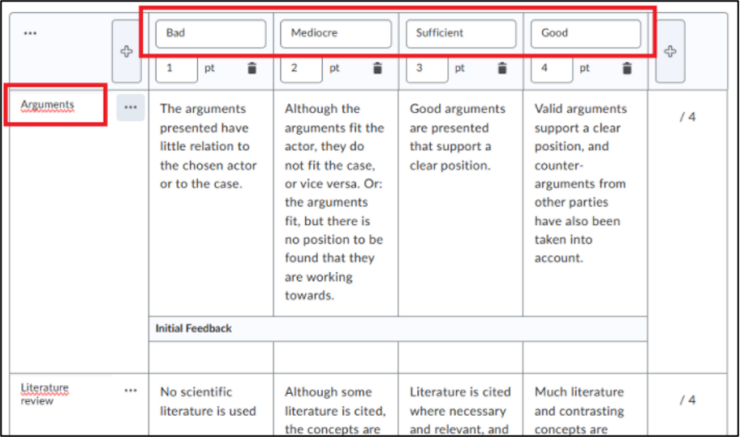
- Now write the assessment criteria for each section.
- You can change the names of these criteria at the top to your own wishes. Also give the separate criteria separate names for each section, such as ‘Introduction, Arguments, Literature Review’, etc. This makes it clear to the student exactly what they are being assessed on.
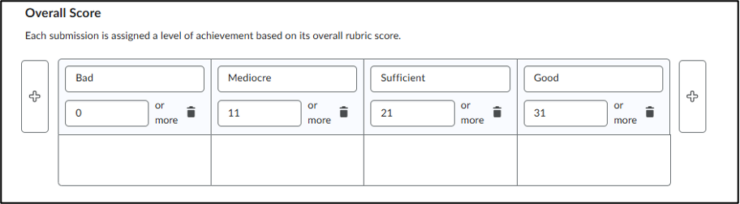
- At the bottom of the page it says ‘Overall Score’. This refers to a summary label that is automatically awarded based on the total number of points obtained on the rubric. If you use an Analytic rubric with points, Brightspace adds up the scores of all criteria. Based on that, it places the total score in a “level of achievement”, such as:
- Bad (0-10 points)
- Mediocre (11-20 points)
- Sufficient (21-30 points)
- Good (31-40 points)
- You can set these levels and associated thresholds yourself in the Overall Score section.
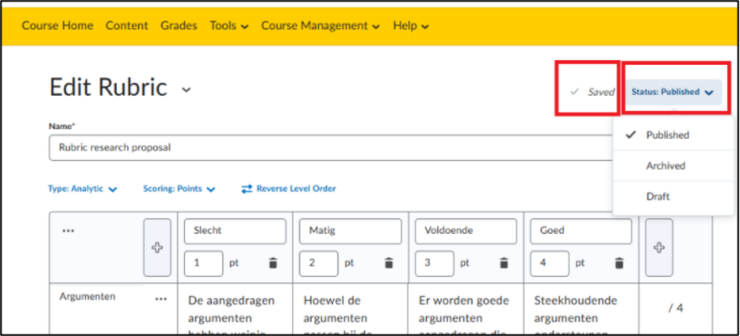
- Your changes are automatically saved throughout the process. You can see that at the very top of the page at Saved.
- You can also choose to publish the rubric immediately by changing the ‘Status’ to ‘Published’, or to keep it ‘Archived’, or as a ‘Draft’ version so that you can continue working on it later.